Department Of Cardiology
Parumala cardiology is a Centre of Excellence in Cardiac Sciences offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic and therapeutic medical technology to ensure high precision diagnosis, accurate treatment and best possible medical outcomes.
Parumala cardiology is committed to clinical excellence, our team of expert doctors provides round-the-clock care, ensuring seamless medical attention at all times. Equipped with a state-of-the-art Cath lab that operates 24/7, we integrate cutting-edge technology with precision-driven therapies to deliver the highest standard of patient care and outcomes.
Parumala cardiology department is home to a highly specialized team
- Seven expert cardiologists
Together, our team provides 24/7 specialized cardiac care, ensuring timely interventions and efficient management of complex cardiac conditions.
Our Doctors
Cardiology
Pioneering Interventional Cardiology
Parumala Cardiology is at the forefront of cardiac interventions, offering a full spectrum of cutting-edge procedures, including:
Conditions like inguinal hernia, hydrocele, circumcision and umbilical hernia can be performed as daycare procedures — with discharge on the same day.
Specialized care for newborns with congenital anomalies and critical conditions with a well-equipped NICU and round-the-clock availability of Neonatologists and experienced Neonatal nursing care.
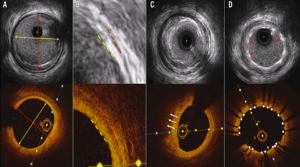
What is OCT?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an advanced, catheter-based imaging technique that
utilizes near-infrared light to generate high-resolution images of the coronary arteries and
stents. It is a valuable tool for diagnosing and managing coronary artery disease (CAD).
How OCT Works
A catheter is inserted into the coronary artery and guided to the area of interest.
Near-infrared light is used to capture detailed cross-sectional images of the artery’s inner layers.
Compared to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), OCT provides significantly higher resolution, allowing for precise assessment of arterial health.
What OCT Reveals
OCT enables cardiologists to visualize the microstructure of coronary arteries with exceptional clarity, including:
Plaque Composition: Differentiates between lipid-rich, calcified, and fibrotic plaques.
Plaque Characteristics: Identifies high-risk, vulnerable plaques prone to rupture.
Stent Apposition and Expansion: Evaluates stent positioning, expansion, and potential
malapposition.
Thrombus Detection: Identifies blood clots within the arterial lumen.
Clinical Applications
Helps pinpoint culprit lesions and assess plaque burden in coronary artery disease.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Optimizes stent deployment and ensures proper apposition for improved outcomes.
Research: Advances the understanding of atherosclerosis and acute coronary syndromes by
providing detailed imaging insights.
With its superior imaging capabilities, OCT plays a crucial role in guiding interventional
cardiology procedures, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing our understanding of
coronary artery disease.
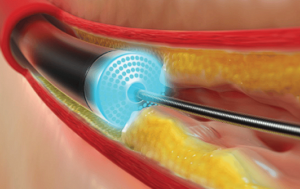
What is IVL?
Intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) is an advanced, minimally invasive technique used to treat
calcified plaques in coronary and peripheral arteries. It utilizes sonic pressure waves to modify hardened arterial blockages, making the vessel more receptive to stent placement.
How It Works
● A catheter is inserted into the affected artery and guided to the calcified area.
● The catheter houses a specialized device that emits controlled sonic pressure waves.
● These waves penetrate the vessel wall, effectively breaking down both superficial and
deep calcium deposits.
● This process enhances vessel compliance, facilitating optimal balloon expansion and
stent placement.
Why IVL Is Used
● Arterial calcification can make it challenging to dilate vessels using conventional balloon
angioplasty.
● IVL helps modify rigid plaques, ensuring better stent expansion and improved procedural
outcomes.
● It is a safe and effective alternative for patients with severe arterial calcification.
Key Benefits
● Suitable for both coronary and peripheral artery disease.
● Effectively treats both superficial and deep calcium deposits.
● Minimally invasive with a favorable safety profile.
● Enhances long-term stent performance by optimizing vessel preparation.
IVL represents a significant advancement in interventional cardiology, offering a targeted and efficient approach to managing complex calcified lesions.
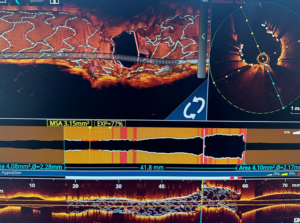
What is Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS)?
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) is an advanced imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to
create detailed, real-time images of the inside of blood vessels, particularly the coronary
arteries. It plays a vital role in diagnosing artery blockages and guiding interventional
procedures like angioplasty and stenting.
How IVUS Works
1. A thin catheter with an ultrasound probe is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the wrist or groin, and guided to the coronary arteries.
2. The ultrasound probe emits high-frequency sound waves, which reflect off the artery walls
and surrounding tissues.
3. These reflections are converted into real-time cross-sectional images, allowing precise
visualization of the vessel’s structure.
Why IVUS is Used
● IVUS provides a comprehensive assessment of coronary artery disease by offering
insights into:
● Plaque Composition and Severity – Identifies different types of plaques and measures their extent.
● Stent Placement and Expansion – Ensures optimal positioning and full expansion of stents during angioplasty.
● Stent Function and Long-Term Monitoring – Detects complications such as restenosis
(re-narrowing) or malapposition.
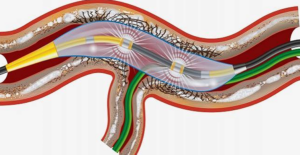
The principle behind rotablation is differential cutting. A rotablator is a flexible catheter with a
tiny diamond-coated burr at the tip. As the diamond-coated burr spins rapidly, it drills into the tough, calcified plaque blocking the artery, breaking it down. The artery’s flexible walls shift aside as the burr works, helping to protect surrounding tissue and reduce the risk of damage. This precise approach clears the blockage while keeping the artery safe. Since 95% of the particles created during rotablation are smaller than 5 microns, the body’s natural clean-up system, called the reticuloendothelial system, is able to remove them safely.
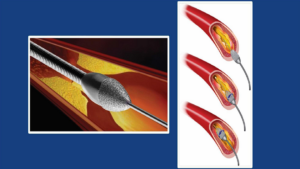
Laser Angioplasty is an advanced and sophisticated technology to open up blocked heart
vessels. It is a lifesaving procedure for patients who had a heart attack.
It is the only technology currently available to dissolve clots within heart blood vessels. Many blood vessel treatments that had been declared untreatable with the angioplasty can now be treatable with Laser Angioplasty.
Laser Angioplasty aims to reduce the chance of open heart surgery and boosts the quality of life
for patients by improve clinical outcomes and reducing the time of stay at the hospital
● Precision with utmost care
● State of the art technology
● Improved quality of life
● Avoids the need for bypass surgery (open heart surgery)
Excimer Laser System
A safe and effective technique as an adjunct to conventional PCI
Excimer laser coronary angioplasty may help to solve some of the problems associated with
treating chronic total occlusions.
Excimer laser catheter can be used to ablate tissue.
Usually, the fat deposition in the coronary blood vessels are treated by Angioplasty where a
balloon will be inserted into the artery and then inflated resulting to expand and loosen the fat
deposits.In Laser Angioplasty, using lasers the plagues are vaporized.
A leadless pacemaker is one which is implanted directly into the heart chamber through a vein
in the leg, eliminating the need for chest incisions or leads (wires). It is designed to be smaller,
more efficient, and less invasive than traditional pacemakers, making it a breakthrough in
cardiac rhythm management.
Long Battery Life: With an estimated battery life of up to 12 -19 years, the LLP offers
long-term reliability and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Automatic Heart Rate Adjustment: The pacemaker features adaptive pacing, meaning it
automatically adjusts the heart rate based on the patient’s activity levels, ensuring optimal
cardiac function.
Implantation in the Right Ventricle: The pacemaker is positioned in the right ventricle, where it
delivers electrical pulses to regulate the heartbeat.
Secure Fixation: The device is anchored to the heart tissue ensuring stability without damaging
heart tissue.
✔ Fewer Complications:
No leads, reducing the risk of lead fractures or infections.
Lower chance of pocket-related complications (such as infections or skin erosion).
✔ Faster Recovery:
No chest incision, leading to a quicker recovery and fewer post-procedure restrictions.
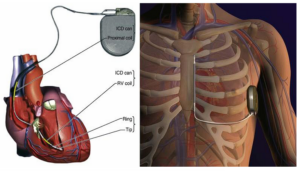
An Automatic Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (AICD) is a small, implanted device that monitors and corrects abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). It functions as both a defibrillator to treat life-threatening arrhythmias and, in many cases, as a pacemaker to regulate slow heartbeats.
What is an AICD?
✔ Purpose:
Designed to detect and treat dangerous heart rhythm disorders, such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, which can lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
✔ How It Works:
● Continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity for irregular rhythms.
● If a life-threatening arrhythmia is detected, it can deliver an electric shock to restore a
normal heartbeat.
● If the heart beats too slowly, some AICDs can function as a pacemaker, sending small electrical pulses to stimulate heartbeats.
Types of AICDs:
1. Traditional ICD:
Leads (wires) are implanted inside the heart to monitor and correct rhythms.
2. Subcutaneous ICD (S-ICD):
Placed under the skin with no leads inside the heart, reducing lead-related complications.
Key Benefits of AICD Therapy:
✔ Prevents sudden cardiac death by delivering life-saving shocks when needed.
✔ Continuously monitors heart rhythms, ensuring rapid response to dangerous arrhythmias.
✔ Can function as a pacemaker to regulate slow heartbeats if necessary.
✔ Improves survival rates in patients at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias.
Overview:
A Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) pacemaker, also known as a biventricular
pacemaker, is a specialized device used to treat heart failure by improving the synchronization
of the heart's ventricles (lower chambers). By delivering precisely timed electrical impulses, CRT enhances the heart’s pumping efficiency and alleviates heart failure symptoms.
How CRT Works:
CRT is designed for patients experiencing delayed electrical conduction in the ventricles, often
indicated by a wide QRS complex on an electrocardiogram (ECG). The device sends mild electrical signals to coordinate the contractions of both ventricles, ensuring they beat in sync, which improves cardiac output and overall heart function.
Key Features of CRT Pacemakers:
● Three Leads for Optimal Synchronization:
● One lead is placed in the right atrium.
● One in the right ventricle.
● One in the left ventricle (via the coronary sinus) to stimulate both ventricles simultaneously.
Biventricular Pacing:
The CRT device ensures that both ventricles contract together, reducing inefficiencies in heart function.
Two Types of CRT Devices:
1. CRT-P (Pacemaker Only): Provides pacing therapy to improve ventricular coordination.
2. CRT-D (Pacemaker + Defibrillator): Includes a built-in defibrillator to treat life-threatening
arrhythmias in high-risk patients.
3. BIV LOT Pacemaker+ defibrillator with additional left bundle pacing leads
Implantation Procedure:
● The CRT device is implanted just below the collarbone through a small incision.
● Leads are carefully positioned in the heart chambers and secured
● The device is programmed to optimize ventricular synchronization.
Benefits of CRT Therapy:
✔ Improved Heart Function: Enhances pumping efficiency and cardiac output.
✔ Symptom Relief: Reduces fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention.
✔ Enhanced Quality of Life: Increases the ability to perform daily activities and exercise.
✔ Fewer Hospitalizations: Lowers the risk of heart failure-related complications and admissions.
Who Should Consider CRT?
CRT is recommended for patients with:
Moderate to severe heart failure symptoms despite optimal medical treatment.
A wide QRS complex (suggesting delayed electrical conduction).
Reduced left ventricular function (weakened heart pumping ability).
Overview:
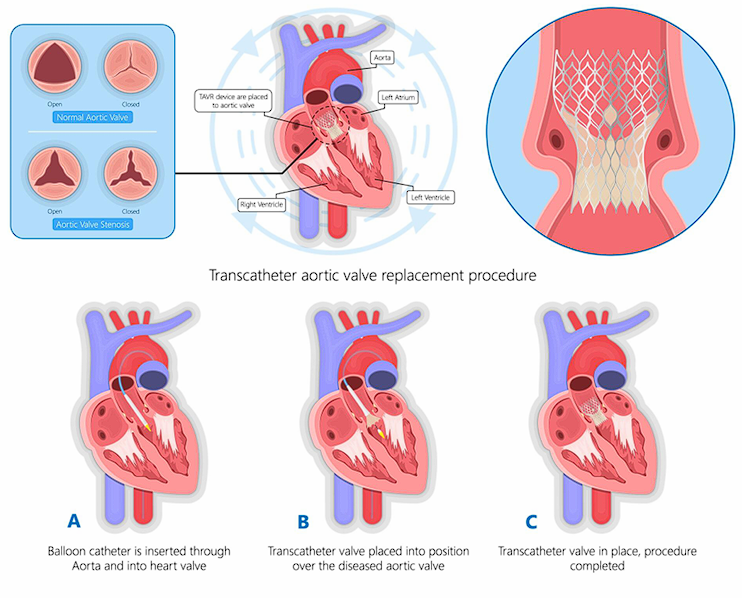
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR), also known as Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), is a minimally invasive procedure designed to replace a diseased aortic valve without an open-heart surgery. It is primarily used to treat severe aortic stenosis, a
condition where the aortic valve becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
Procedure:
1. Accessing the Heart:
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the femoral artery in the leg or, in some cases, through the subclavian artery or the apex of the heart.
2. Valve Placement:
The artificial valve, which is mounted on a collapsible stent, is carefully guided through the catheter to the diseased aortic valve.
3. Deployment of the New Valve:
Once positioned correctly, the new valve expands, pushing the old valve’s leaflets aside and taking over its function to restore normal blood flow.
Who Needs TAVR?
TAVR is an effective treatment for patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, particularly those who are:
High-risk or ineligible for open-heart surgery due to age, frailty, or other medical conditions.
Looking for a less invasive alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR).
Benefits of TAVR:
Minimally invasive – avoids large chest incisions.
Shorter hospital stay
Reduced recovery time
Lower risk of complications compared to open-heart surgery in high-risk patients.
- 2D & 3D Echocardiography
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE)
Continuous ECG Monitoring
- Holter monitoring
- Implantable Loop Recorder
Device closure for congenital heart diseases (ASD, PDA, VSD)
1. Accessing the Heart:
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the femoral artery in the leg or, in some cases, through the subclavian artery or the apex of the heart.
2. Valve Placement:
The artificial valve, which is mounted on a collapsible stent, is carefully guided through the catheter to the diseased aortic valve.
3. Deployment of the New Valve:
Once positioned correctly, the new valve expands, pushing the old valve’s leaflets aside and taking over its function to restore normal blood flow.
- Minimally invasive – avoids large chest incisions
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced recovery time
- Lower risk of complications compared to open-heart surgery in high-risk patients.
Parumala Hospital of excellence in Cardiac Sciences is the facility of Cathlab with a state of the art electrophysiology lab/Intravascular ultrasound, fractional flow reserve estimate and rotablation
- Low radiation clarity Cathlab
Parumal Hospital delivers 24×7 primary angioplasty programs with perfect logistics. We have a well functioning Cathlab with newer coronary imaging modalities. Coronary physiology assessment by FFR and facilities of rot ablation for complex angioplasty are also available.
- 24x7 Primary Angioplasty
- Elective angioplasty including complex procedures
- Peripheral Angiogram
- Peripheral Interventions
- Device closures(ASD, VSD, PDA)
- Pacemakers
- Intra cardiac Defibrillators
- Electrophysiological study & ablation
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Left & Right heart catheterization
- Balloon Valvulotomies(BMV,BAV,PPV)
- Endovascular interventions
Cardiology Contact Number: 9070119070
Cardiology Contact Email: procardiology@parumalahospital.com
Research & Academic Excellence
The Parumala Cardiology Department is committed to excellence not only in patient care but also in research, education, and innovation. Our team actively engages in groundbreaking cardiovascular research, contributing to medical advancements that shape the future of cardiology. With a strong focus on teaching, we nurture the next generation of cardiologists through specialized training programs, hands-on clinical experience, and academic collaborations
At PICC, we are committed to setting new standards in cardiovascular medicine by combining innovation, expertise, and compassionate care to achieve exceptional clinical outcomes.
Experience world-class cardiac care at PICC—where technology meets excellence.