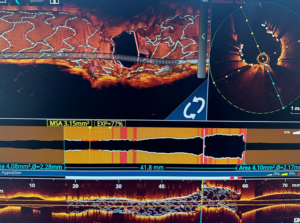
What is OCT?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an advanced, catheter-based imaging technique that
utilizes near-infrared light to generate high-resolution images of the coronary arteries and
stents. It is a valuable tool for diagnosing and managing coronary artery disease (CAD).
How OCT Works
A catheter is inserted into the coronary artery and guided to the area of interest.
Near-infrared light is used to capture detailed cross-sectional images of the artery’s inner layers.
Compared to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), OCT provides significantly higher resolution, allowing for precise assessment of arterial health.
What OCT Reveals
OCT enables cardiologists to visualize the microstructure of coronary arteries with exceptional clarity, including:
Plaque Composition: Differentiates between lipid-rich, calcified, and fibrotic plaques.
Plaque Characteristics: Identifies high-risk, vulnerable plaques prone to rupture.
Stent Apposition and Expansion: Evaluates stent positioning, expansion, and potential
malapposition.
Thrombus Detection: Identifies blood clots within the arterial lumen.
Clinical Applications
Helps pinpoint culprit lesions and assess plaque burden in coronary artery disease.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Optimizes stent deployment and ensures proper apposition for improved outcomes.
Research: Advances the understanding of atherosclerosis and acute coronary syndromes by
providing detailed imaging insights.
With its superior imaging capabilities, OCT plays a crucial role in guiding interventional
cardiology procedures, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing our understanding of
coronary artery disease.
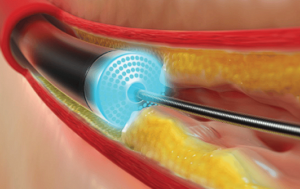
What is IVL?
Intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) is an advanced, minimally invasive technique used to treat
calcified plaques in coronary and peripheral arteries. It utilizes sonic pressure waves to modify hardened arterial blockages, making the vessel more receptive to stent placement.
How It Works
● A catheter is inserted into the affected artery and guided to the calcified area.
● The catheter houses a specialized device that emits controlled sonic pressure waves.
● These waves penetrate the vessel wall, effectively breaking down both superficial and
deep calcium deposits.
● This process enhances vessel compliance, facilitating optimal balloon expansion and
stent placement.
Why IVL Is Used
● Arterial calcification can make it challenging to dilate vessels using conventional balloon
angioplasty.
● IVL helps modify rigid plaques, ensuring better stent expansion and improved procedural
outcomes.
● It is a safe and effective alternative for patients with severe arterial calcification.
Key Benefits
● Suitable for both coronary and peripheral artery disease.
● Effectively treats both superficial and deep calcium deposits.
● Minimally invasive with a favorable safety profile.
● Enhances long-term stent performance by optimizing vessel preparation.
IVL represents a significant advancement in interventional cardiology, offering a targeted and efficient approach to managing complex calcified lesions.
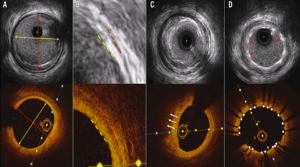
What is Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS)?
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) is an advanced imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to
create detailed, real-time images of the inside of blood vessels, particularly the coronary
arteries. It plays a vital role in diagnosing artery blockages and guiding interventional
procedures like angioplasty and stenting.
How IVUS Works
1. A thin catheter with an ultrasound probe is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the wrist or groin, and guided to the coronary arteries.
2. The ultrasound probe emits high-frequency sound waves, which reflect off the artery walls
and surrounding tissues.
3. These reflections are converted into real-time cross-sectional images, allowing precise
visualization of the vessel’s structure.
Why IVUS is Used
● IVUS provides a comprehensive assessment of coronary artery disease by offering
insights into:
● Plaque Composition and Severity – Identifies different types of plaques and measures their extent.
● Stent Placement and Expansion – Ensures optimal positioning and full expansion of stents during angioplasty.
● Stent Function and Long-Term Monitoring – Detects complications such as restenosis
(re-narrowing) or malapposition.
The principle behind rotablation is differential cutting. A rotablator is a flexible catheter with a
tiny diamond-coated burr at the tip. As the diamond-coated burr spins rapidly, it drills into the tough, calcified plaque blocking the artery, breaking it down. The artery’s flexible walls shift aside as the burr works, helping to protect surrounding tissue and reduce the risk of damage. This precise approach clears the blockage while keeping the artery safe. Since 95% of the particles created during rotablation are smaller than 5 microns, the body’s natural clean-up system, called the reticuloendothelial system, is able to remove them safely.
Laser Angioplasty is an advanced and sophisticated technology to open up blocked heart
vessels. It is a lifesaving procedure for patients who had a heart attack.
It is the only technology currently available to dissolve clots within heart blood vessels. Many blood vessel treatments that had been declared untreatable with the angioplasty can now be treatable with Laser Angioplasty.
Laser Angioplasty aims to reduce the chance of open heart surgery and boosts the quality of life
for patients by improve clinical outcomes and reducing the time of stay at the hospital
● Precision with utmost care
● State of the art technology
● Improved quality of life
● Avoids the need for bypass surgery (open heart surgery)
Excimer Laser System
A safe and effective technique as an adjunct to conventional PCI
Excimer laser coronary angioplasty may help to solve some of the problems associated with
treating chronic total occlusions.
Excimer laser catheter can be used to ablate tissue.
Usually, the fat deposition in the coronary blood vessels are treated by Angioplasty where a
balloon will be inserted into the artery and then inflated resulting to expand and loosen the fat
deposits.In Laser Angioplasty, using lasers the plagues are vaporized.