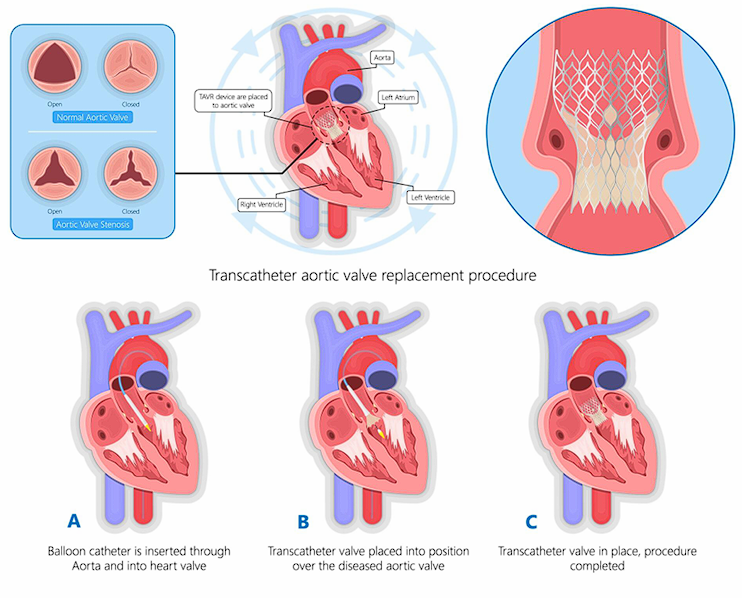
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR), also known as Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), is a minimally invasive procedure designed to replace a diseased aortic valve without an open-heart surgery. It is primarily used to treat severe aortic stenosis, a
condition where the aortic valve becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
1. Accessing the Heart:
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the femoral artery in the leg or, in some cases, through the subclavian artery or the apex of the heart.
2. Valve Placement:
The artificial valve, which is mounted on a collapsible stent, is carefully guided through the catheter to the diseased aortic valve.
3. Deployment of the New Valve:
Once positioned correctly, the new valve expands, pushing the old valve’s leaflets aside and taking over its function to restore normal blood flow.
- Minimally invasive – avoids large chest incisions
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced recovery time
- Lower risk of complications compared to open-heart surgery in high-risk patients.